Agenda setting in journalism is reality constructed, or mediated, by
social life. The four areas are public, policy, corporate and media. Public
refers to topics the public place importance on, policy is the issues decision
makers think are important, issues big businesses and corporations believe are
important come under corporate and media relates to the issues discussed in the
media. These four areas are all integrated.
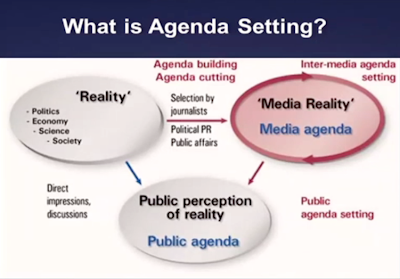 The mass media not only report events, but also filters and shapes it to
fit a particular mould. Through media concentration on a few issues, the public
perceives these issues as having a higher importance than they possibly do. For
example, the media frenzy over Alan Jones’ comments, instead of perhaps
focusing on the more important issues that are happening in the Middle East. The
idea of agenda setting has been around for a while; in the 1920s, there was the
concept of a ‘Magic Bullet’ that injected direct influence into the audience. Adolf
Hitler and Leni Riefenstahl successfully used images to manipulate German
perception of Hitler as a great leader and in 1968 during the US presidential
campaign it was researched that an undecided voter could be persuaded by the
mass medias emphasis on certain topics.
The mass media not only report events, but also filters and shapes it to
fit a particular mould. Through media concentration on a few issues, the public
perceives these issues as having a higher importance than they possibly do. For
example, the media frenzy over Alan Jones’ comments, instead of perhaps
focusing on the more important issues that are happening in the Middle East. The
idea of agenda setting has been around for a while; in the 1920s, there was the
concept of a ‘Magic Bullet’ that injected direct influence into the audience. Adolf
Hitler and Leni Riefenstahl successfully used images to manipulate German
perception of Hitler as a great leader and in 1968 during the US presidential
campaign it was researched that an undecided voter could be persuaded by the
mass medias emphasis on certain topics.
The agenda setting family has seven parts, these are media gate keeping,
media advocacy, agenda cutting, agenda setting ‘bandwagon’, the diffusion of
news, portray of an issue and media dependence.
1)
Media gate keeping: “How individuals control the flow of messages through a communication
channel.” For example in the US Fox is more of a right wing station and
thus is more likely to promote Mitt Romney in this years presidential campaign
2)
Media advocacy: the purposeful promotion of a message
through the media, e.g. health issues like smoking, obesity, binge drinking
3)
Agenda cutting: a lot of the truth of reality that is
going on th the world isn’t represented, for example, AIDS is on the increase
but this huge issues has taken a backseat to other news events as it is not
desirable to the public and not as enticing to the majority of society than
Justin Beiber’s haircut
4)
Agenda setting ‘bandwagon’: when the media follows the
current trend or ‘surfs’ the wave of topics bought up in different media spheres.
Two such events this year are the Kony 2012 campaign and more recently the PSY
‘Gangnam Style’ song and dance
5)
Diffusion of news: the process through which an
important event is communicated to the public i.e., how, where and when news is
released
6)
Portray of an issue: the way an issue is portrayed is
often how the public, or the uneducated part of the public, perceives it
7)
Media dependence: the more dependant a person is on
media for information the more susceptible that person becomes.

One example of agenda setting is the prevalence of climate change in the
news over the past 25 years. Referred to as the “Greenhouse Effect” in 1988 by
The Age the same concept is now know as climate change, and is still an issue
that is often raised in the media.

No comments:
Post a Comment